The Thermal Expansion Tank: Protecting Your Water Heater and Plumbing from Pressure Damage

Introduction to Thermal Expansion in Plumbing Systems
In modern homes, your water heater works tirelessly to provide hot water for showers, dishes, and laundry. But have you ever considered the hidden pressures building within your plumbing? Thermal expansion is a natural phenomenon where water expands as it heats up, and in closed systems, this can lead to dangerous pressure spikes. Without proper management, it risks damaging your water heater, pipes, and fixtures. That's where the thermal expansion tank comes in – a simple yet essential component that absorbs excess pressure, ensuring longevity and safety.
Safeguard Your Plumbing System – Get Your Quote
As a trusted plumbing expert, we're here to reassure you: understanding and addressing thermal expansion is straightforward. This article dives deep into how these tanks protect your system, why they're often overlooked, and when you might need one. By the end, you'll feel confident in safeguarding your home's plumbing.
Understanding Thermal Expansion: The Science Behind the Pressure
Water doesn't just heat up; it physically expands. When your water heater raises the temperature from, say, 50°F to 120°F, the volume of water can increase by up to 2-3%. In an open system, this expanded water could flow back into the municipal supply. However, most homes today feature closed water systems due to building codes and efficiency standards.
What makes a system "closed"? It's often the installation of check valves or pressure-reducing valves (PRVs) that prevent backflow. These valves are great for maintaining consistent pressure and protecting against contamination, but they trap the expanding water inside your pipes. Without an escape route, pressure can surge from a normal 50-80 psi to over 150 psi – levels that strain your entire plumbing network.
Imagine filling a balloon with more air than it can handle; eventually, something gives. In plumbing, this "give" could mean leaks, bursts, or premature failure of your water heater's tank. But don't worry – recognizing this early prevents costly repairs.
The Dangers of Unchecked Pressure in Closed Systems
Ignoring thermal expansion isn't just inconvenient; it's a recipe for disaster. High pressure silently stresses your water heater's internal components, leading to cracks in the tank lining or weakened welds. Over time, this can cause:
- Leaky fixtures: Faucets and toilets may drip or fail prematurely due to constant pressure fluctuations.
- Damaged appliances: Dishwashers and washing machines endure extra wear, shortening their lifespan.
- Burst pipes: In extreme cases, pipes can rupture, causing water damage and expensive emergencies.
- Safety valve discharges: Your temperature and pressure (T&P) relief valve might release water frequently, signaling overload – a clear red flag.
Statistics from plumbing associations show that water heater failures account for thousands of insurance claims annually, many linked to pressure issues. The good news? Installing a thermal expansion tank mitigates these risks effectively, often extending your water heater's life by years. It's a proactive step that pays off in peace of mind and savings.
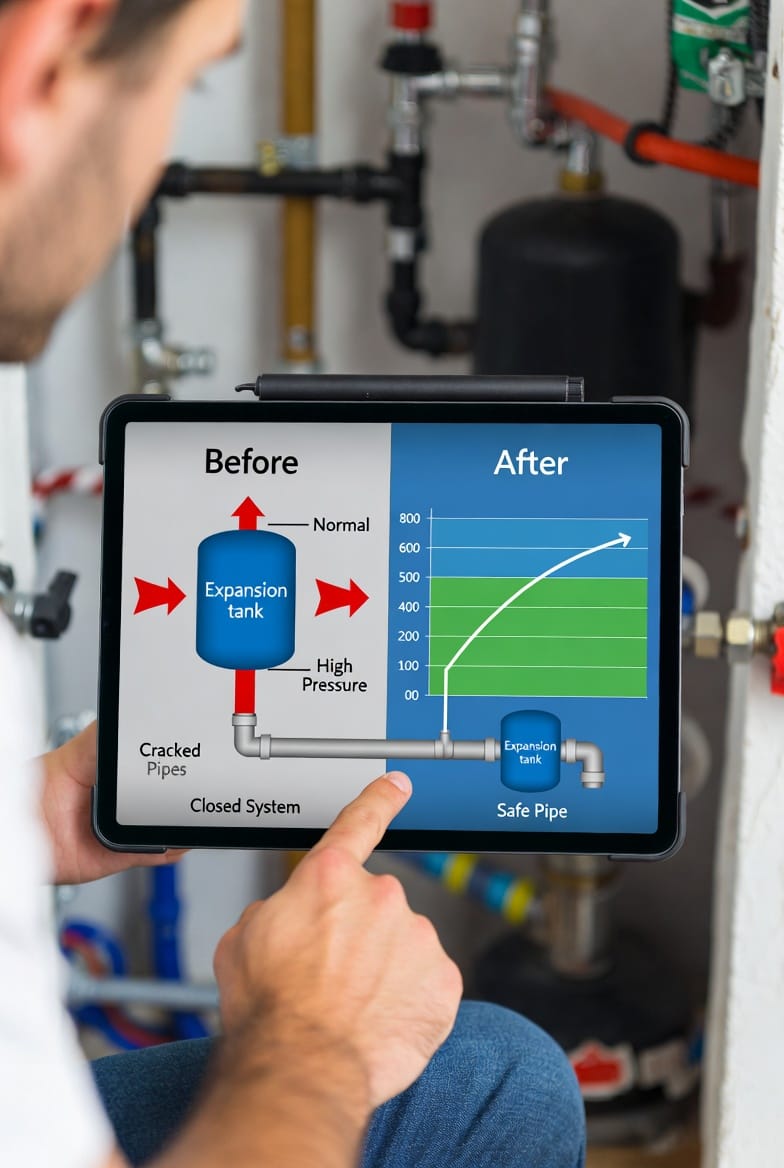
How a Thermal Expansion Tank Works: Absorbing the Excess
At its core, a thermal expansion tank is a small, bladder-equipped vessel connected to your water heater's cold water inlet. Inside, it's divided into two chambers: one for water and one for compressed air. As water heats and expands, it pushes into the tank's water chamber, compressing the air cushion on the other side. This absorption prevents pressure from building in the main system.
Think of it as a shock absorber for your plumbing. Without it, expanding water has nowhere to go, forcing pressure upward. With it, the system remains balanced. Most tanks are pre-charged with air at around 40-60 psi, matching your home's water pressure, and they're sized based on your water heater's capacity – typically 2-5 gallons for residential use.
Installation is quick and non-invasive, usually taking a professional plumber less than an hour. It's connected via a tee fitting on the cold line, above the heater to allow for proper drainage if needed. Rest assured, these tanks are durable, made from steel with a rubber diaphragm that separates water from air, preventing corrosion.
Benefits of Installing an Expansion Tank
Why invest in this often-missed component? The advantages are clear and multifaceted:
- Extended equipment life: By stabilizing pressure, your water heater avoids the "silent stress" of constant expansion cycles, potentially adding 5-10 years to its service.
- Energy efficiency: Stable systems run more smoothly, reducing energy waste from overworked components.
- Cost savings: Prevent repairs that could cost hundreds or thousands – a tank installation is a fraction of replacing a burst heater.
- Code compliance: Many local building codes now require expansion tanks in closed systems, ensuring your home meets safety standards.
- Peace of mind: No more worrying about mysterious leaks or T&P valve discharges; your system is protected.
Homeowners who've added tanks report fewer issues, with one study from the Plumbing-Heating-Cooling Contractors Association noting a 40% drop in pressure-related service calls. It's an upgrade that's as practical as it is reassuring.
Signs You Need a Thermal Expansion Tank
Not sure if your system is at risk? Look for these indicators:
- Presence of a PRV or check valve: If your home has these, it's likely a closed system.
- Frequent T&P valve releases: Hearing water discharge from your heater's safety valve? That's excess pressure escaping.
- Fluctuating water pressure: Inconsistent flow from taps could signal buildup.
- Aging water heater: Older models are more vulnerable without modern protections.
- Recent plumbing upgrades: New fixtures or valves might have closed your system unknowingly.
If any apply, a quick inspection can confirm. Professional plumbers use gauges to measure pressure spikes during heating cycles, providing data-driven recommendations.

Installation and Maintenance: Keeping Your System Safe
Ready to install? Here's a step-by-step overview (always hire a licensed professional for safety):
- Assessment: Check your system's pressure and confirm it's closed.
- Sizing: Select a tank based on heater volume – e.g., 40-gallon heater needs a 2-gallon tank.
- Placement: Mount above the heater on the cold line for gravity assistance.
- Connection: Use dielectric unions to prevent corrosion.
- Testing: Charge the air side to match incoming pressure, then test for leaks.
Maintenance is minimal: Annually check the air pressure with a tire gauge (valve on the tank) and ensure the bladder isn't waterlogged. If pressure drops, recharge it. With proper care, tanks last 5-10 years.
Common Myths and Misconceptions Debunked
Myth: "My system doesn't need one because it's old." Reality: Older systems can benefit most, as they're prone to failures.
Myth: "Expansion tanks are expensive." Reality: Costs range from $50-150 for the tank, plus installation – far less than repairs.
Myth: "I can DIY this." Reality: Improper installation risks voids warranties; pros ensure compliance.
We're here to clarify: Expansion tanks are a smart, low-maintenance solution for modern plumbing challenges.
Conclusion: Safeguard Your Home Today
Thermal expansion might be invisible, but its impacts aren't. By installing a thermal expansion tank, you protect your water heater and plumbing from pressure damage, ensuring reliable hot water without the worry. It's a critical component that's often missed but easily addressed.
Protect your water heater from silent stress. Ready to check your system?
Protect Against Thermal Expansion – Free Consultation Now


